Diamond Price Prediction#
Demo website#
Diamond Price Prediction - Built with Streamlit and deployed on Streamlit Cloud.
Packages#
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
Import datasets from Kaggle#
This dataset is available on Kaggle at Diamond Price Prediction.
diamond_df = pd.read_csv('data/diamonds.csv')
diamond_df.head(), diamond_df.shape
Eliminate the leftmost column, which is just an index.
diamond_df = diamond_df.drop(['Unnamed: 0'], axis=1)
Data Exploration#
Print first few rows, shape, and data types#
diamond_df.head(), diamond_df.shape, diamond_df.dtypes
Use describe() to get summary statistics#
diamond_df.describe()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
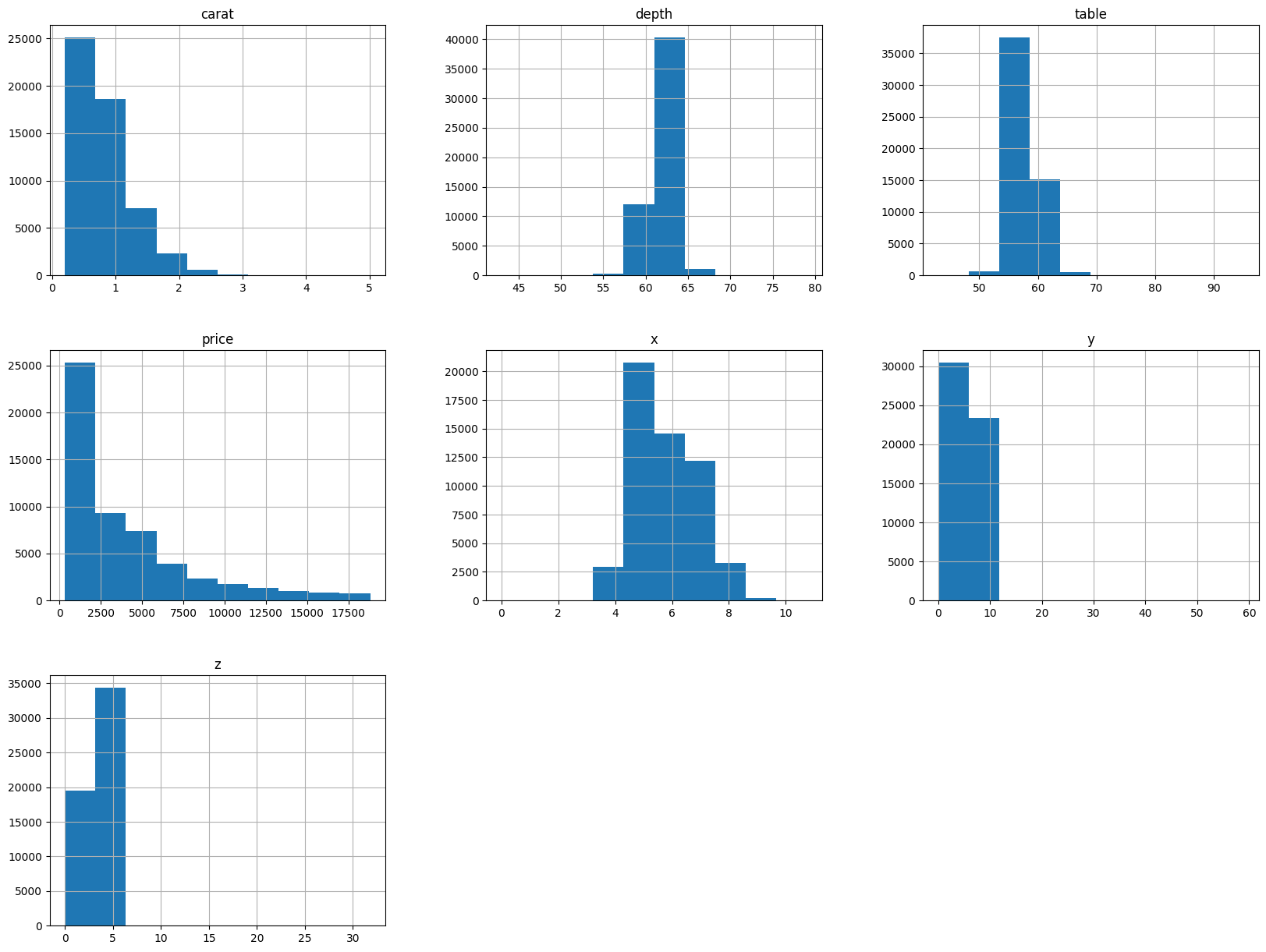
# Print 7 histograms, with each title describe shortly the distribution style of the data (e.g. right-skewed, clustered,...)
diamond_df.hist(figsize=(20, 15));
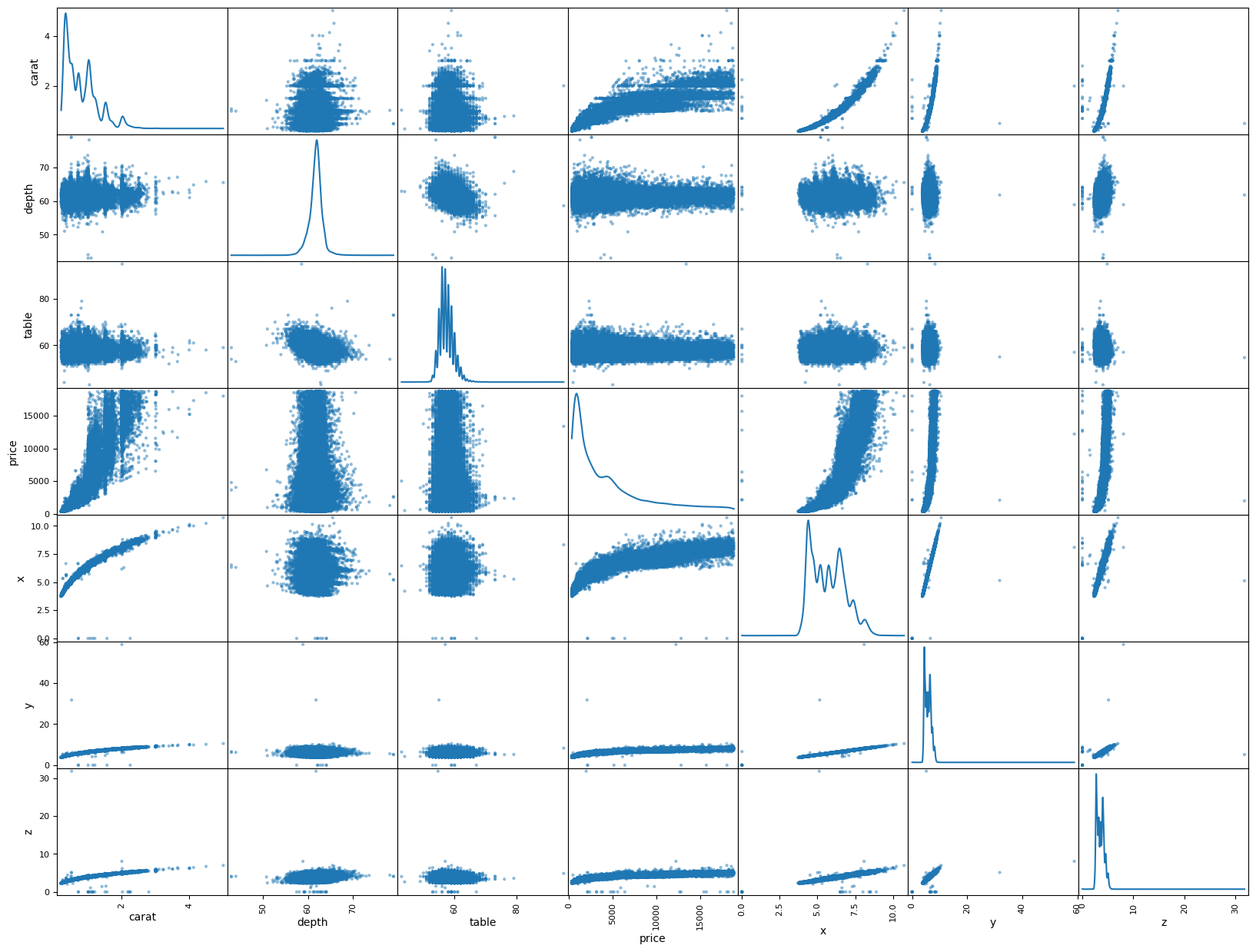
# The scatter matrix is a great way to visualize the relationships between multiple variables in a dataset.
from pandas.plotting import scatter_matrix
scatter_matrix(diamond_df, figsize=(20, 15), diagonal='kde');
Data Preparation#
Manipulate categorical variables#
diamond_df['cut'].unique(), diamond_df['color'].unique(), diamond_df['clarity'].unique()
color_mapping = {'J': 0, 'I': 1, 'H': 2, 'G': 3, 'F': 4, 'E': 5, 'D': 6}
diamond_df.color = diamond_df.color.map(color_mapping)
clarity_mapping = {'I1': 0, 'SI2': 1, 'SI1': 2, 'VS2': 3, 'VS1': 4, 'VVS2': 5, 'VVS1': 6, 'IF': 7}
diamond_df.clarity = diamond_df.clarity.map(clarity_mapping)
cut_mapping = {'Fair': 0, 'Good': 1, 'Very Good': 2, 'Premium': 3, 'Ideal': 4}
diamond_df.cut = diamond_df.cut.map(cut_mapping)
diamond_df.describe()
Eliminate disturbing values#
diamond_df = diamond_df.drop(diamond_df[diamond_df["x"]==0].index)
diamond_df = diamond_df.drop(diamond_df[diamond_df["y"]==0].index)
diamond_df = diamond_df.drop(diamond_df[diamond_df["z"]==0].index)
Eliminate values that > 99% of the rest#
diamond_df = diamond_df[diamond_df['depth'] < diamond_df['depth'].quantile(0.99)]
diamond_df = diamond_df[diamond_df['table'] < diamond_df['table'].quantile(0.99)]
diamond_df = diamond_df[diamond_df['x'] < diamond_df['x'].quantile(0.99)]
diamond_df = diamond_df[diamond_df['y'] < diamond_df['y'].quantile(0.99)]
diamond_df = diamond_df[diamond_df['z'] < diamond_df['z'].quantile(0.99)]
diamond_df.head(10)
diamond_df.describe()
X = diamond_df.drop(['price'], axis=1)
y = diamond_df['price']
X = X.to_numpy()
y = y.to_numpy()
X.shape, y.shape
Data for Training and Testing#
Split dataset into 80% training and 20% testing.
X_train = X[:int(X.shape[0]*0.8)]
y_train = y[:int(X.shape[0]*0.8)]
X_test = X[int(X.shape[0]*0.8):]
y_test = y[int(X.shape[0]*0.8):]
Normailize the data by subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation.
xmean = np.mean(X_train, axis=0)
xstd = np.std(X_train, axis=0)
X_train = (X_train - xmean) / xstd
X_test = (X_test - xmean) / xstd
X_train.shape, X_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape
Tranpose the data so that each row is a feature and each column is an example.
X_train = np.hstack([np.ones((X_train.shape[0], 1)), X_train])
X_test = np.hstack([np.ones((X_test.shape[0], 1)), X_test])
X_train.shape, X_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape
Modeling#
Linear Regression Model#
N = X_train.shape[0]
n_epochs = 1000
m = 1000
learning_rate = 0.001
# No explicit bias term; the first column of X_* is ones to learn the intercept via W
theta = np.random.randn(10, 1)
losses = []
Training#
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
for i in range(0, N, m):
# Take a batch of data
X_batch = X_train[i:i+m, :]
y_batch = y_train[i:i+m].reshape(-1, 1)
# Predict y_hat
y_hat = X_batch @ theta
# Compute loss
loss = np.mean((y_hat - y_batch) ** 2)
losses.append(loss)
# Compute gradient
gradient = 2 * X_batch.T @ (y_hat - y_batch)
# Update weights
theta -= learning_rate * (gradient / m)
if (epoch + 1) % 50 == 0:
print(f"Epoch {epoch + 1}/{n_epochs} - Loss: {losses[-1]}")
# Validate the model, compute MSE on the test set
y_hat_test = X_test @ theta
test_loss_mse = np.mean((y_test - y_hat_test) ** 2)
print(f"Test MSE: {test_loss_mse}")
# MAE
test_loss_mae = np.mean(np.abs(y_test - y_hat_test))
print(f"Test MAE: {test_loss_mae}")
# Save the model parameters
np.savez(
'weight.npz',
x_mean=xmean,
x_std=xstd,
theta=theta
)
# Save the training and testing data
np.savez('data.npz', X_train=X_train, y_train=y_train, X_test=X_test, y_test=y_test)